Difference Between RAM and ROM / RAM vs ROM: Today I’m going to tell You About Difference between Random Access Memory and Read Only Memory. So Let’s come to the point and read about RAM and ROM.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
When people talk about computer memory, they usually mean the volatile RAM memory. RAM is a volatile memory and requires power to keep the data accessible. If the computer is turned off, all data contained in RAM is lost. Alternatively referred to as main memory, primary memory or system memory, RAM (random-access memory) is a hardware device that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a computer. It is super-fast and temporary data storage space that a computer needs to access right now or in the next few moments.
Physically, this memory consists of some integrated circuit (IC) chips either on the motherboard or on a small circuit board attached to the motherboard.
A computer’s motherboard is designed in a manner that its memory capacity can be enhanced easily by adding more memory chips.
Hence, if you decide to have more memory than your computer currently has, you can buy more memory chips and plug them in the empty memory slots on the motherboard. Service engineers normally do this job. The additional RAM chips, which plug into special sockets on the motherboard, are known as single in-line memory modules (SIMMs).
RAM stores data for short term use and hence known as temporary memory. Short term memory can be refreshed with information, when the RAM fills up, the processor goes to the hard disk to overlay the old data in Ram with new data.
Types of RAM
There are basically two types of RAM-
- Dynamic Ram (DRAM)
- Static Ram (SRAM)
DYNAMIC RAM
The term dynamic indicates that the memory must be constantly refreshed or it will lose its contents. DRAM is typically used for the main memory in computing devices.
STATIC RAM
SRAM is said to be static because it doesn’t need to be refreshed, unlike dynamic RAM, which needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second. As a result, SRAM is faster than DRAM. Due to these advantages associated with the use of SRAM, It is primarily used for system cache memory, and high-speed registers, and small memory banks such as a frame buffer on graphics cards.
Also Read: 100 + Computer Short Keys Notes
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
A special type of RAM, called read-only memory (ROM), is a non-volatile memory chip in which data is stored permanently and cannot be altered by usual programs.
In fact, storing data permanently into this kind of memory is called “burning in the data” because data in such memory is stored by using fuse-links. Once a fuse-link is burnt, it is permanent. Data stored in a ROM chip can only be read and used – they cannot be changed. This is the reason why it is called read-only memory (ROM). Since ROM chips are non-volatile, data stored in a ROM are not lost when power is switched off or interrupted unlike in the case of a volatile RAM chip. ROMs are also known as field stores, permanent stores, or dead stores.
ROMs are mainly used to store programs and data that do not change and are frequently used. Most basic computer operations are carried out by wired electronic circuits. However, several higher-level and frequently used operations require very complicated electronic circuits for their implementation. Hence, instead of building electronic circuits for these operations, special programs are written to perform them. These programs are called micro-programs because they deal with low-level machine functions and are essentially substitutes for additional hardware.
ROMs are used by computer manufacturers to store these micro-programs so that they cannot be modified by the users.
Also Read: What is SSH and SSH Port and SSH Port Number
A good example of a micro-program is the set of instructions needed to make a computer system ready for use when it is powered on. This micro-program, called “system boot program“, contains a set of start-up instructions to check if the system hardware like memory, I/O devices, etc. are functioning properly.
It looks for an operating system and loads its core part in the volatile RAM of the system to produce the initial display-screen prompt. Note that this micro-program is used every time the computer is switched on and needs to be retained when the computer is switched off. Hence, ROM is an ideal storage for storing it.
Types of ROM
There are basically two types of ROM-
- Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM)
- Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory(EPROM)
PROGRAMMABLE READ-ONLY MEMORY (PROM)
There are two types of read-only memory (ROM) – manufacturer-programmed and user-programmed. A manufacturer-programmed ROM is one in which data is burnt in by the manufacturer of the electronic equipment in which it is used.
For example, a personal computer manufacturer may store the system boot program permanently in a ROM chip located on the motherboard of each PC manufactured by it. Similarly, a printer manufacturer may store the printer controller software in a ROM chip located on the circuit board of each printer manufactured by it. Manufacturer-programmed ROMs are used mainly in those cases where the demand for such programmed ROMs is large. Note that manufacturer-programmed ROM chips are supplied by the manufacturers of electronic equipment and it is not possible for a user to modify the programs or data stored in a ROM chip. On the other hand, a user-programmed ROM is one in which a user can load and store “read-only” programs and data.
That is, it is possible for a user to “customize” a system by converting his/her programs to micro-programs and storing them in a user-programmed ROM chip. Such a ROM is commonly known as Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM) because a user can program it. Once the user programs are stored in a PROM chip they can be executed usually in a fraction of the time previously required. PROMs are programmed to record information using a special device known as PROM-programmer.
However, once the chip has been programmed, the PROM becomes a ROM. That is, the information recorded in it can only be read (it cannot be changed). PROM is also non-volatile storage, i.e., the stored information remains intact even if power is switched off or interrupted.
ERASABLE PROGRAMMABLE READ-ONLY MEMORY (EPROM)
Once information is stored in a ROM or PROM chip it cannot be altered. Erasable Programmable Read Memory (EPROM) overcomes this problem. As the name implies, it is possible to erase information stored in an EPROM chip and the chip can be reprogrammed to store new information.
EPROMs are often used by R&D personnel (experimenters) who frequently change the micro-programs to test the efficiency of a computer with new programs. EPROMs are also useful for those applications in which one may like to store a program in a ROM that would normally not change but under some unforeseen conditions, one may like to alter it. When EPROM is in use, information stored in it can only be “read” and the information remains in the chip until it is erased.
Also Read: Difference Between SSH and SSL / SSH VS SSL
EPROM chips are of two types – one in which the stored information is erased by exposing the chip for some time to ultraviolet light and the other one in which the stored information is erased by using high voltage electric pulses. The former is known as UltraViolet EPROM (UVEPROM) and the latter is known as Electrically EPROM (EEPROM). It is easier to alter information stored in an EEPROM chip as compared to an UVEPROM chip. EEPROM is also known as flash memory because of the ease with which programs stored in it can be altered.
Flash memory is used in many new I/O and storage devices like USB (Universal Serial Bus) pen drive and MP3 music player.
Difference Between RAM and ROM
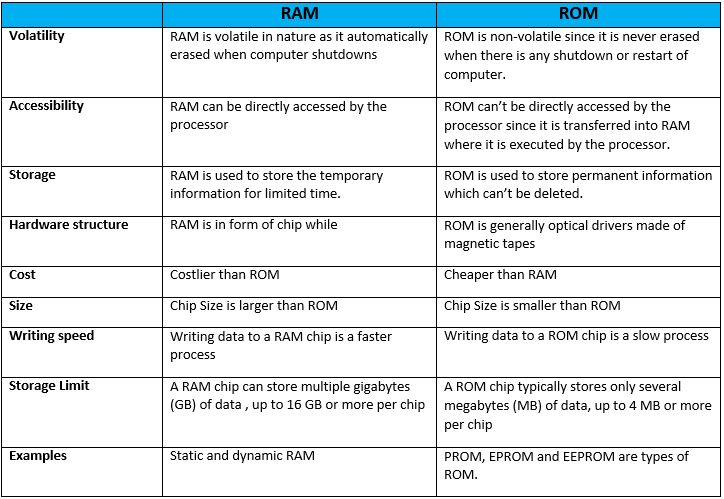
so I am giving you the chart of difference between RAM ans ROM. You can Read difference from this chart.
RAM | ROM |
1- RAM stands for Random Access Memory. | ROM stands for Read Only Memory. |
2- It allows both read and write operations. | It allows only read operations. |
3. It is volatile memory | 3. It is a non volatile memory. |
4. It has large size memory space with higher capacity. | 4. It has small size memory space with less capacity |
5. Memory cell is in the form of flip flop. | 5. Memory cell is in the form of unidirectional contact. |
6. Data in RAM can be modified. | 6. Data in ROM can’t be modified. |
7. It is used to store temporary data and programs. | 7. It is used to store permanent data and permanent programs. |
8. The second operation after booting process is performed in RAM. | 8. The first operation in computer system is performed in ROM (during booting process). |
9. It is used to store data/instructions while they are being processed, waiting to be processed and after being processed before it is provided to output components. | 9. It is used to store program that are required for the operation of electronic devices. |
10. RAM is costlier memory. | 10. It is comparatively cheaper than RAM. |
11. It is used for buffering purpose. | 11. It is not used for buffering purpose. |
12. It is very fast but uses a lot of power. | 12. Fast but uses very little power. |
13. Used in CPU cache, primary memory. | 13. Used in firmware, microcontrollers. |
Read More Differences at Learn Glad.
Tags: RAM vs ROM, Difference between RAM and ROM, RAM and ROM, About RAM and ROM, RAM and ROM wiki, RAM and ROM Notes.